Understanding Dopamine:
The Neurotransmitter That Influences Movement, Pleasure, and Behaviour
Dopamine is a crucial neurotransmitter that plays a pivotal role in various aspects of human functioning, including movement, pleasure, motivation, and behavior. It acts as a chemical messenger, transmitting signals between nerve cells in the brain and between the brain and the rest of the body.
Dopamine’s Role in Movement Control
One of the most well-established functions of dopamine is its involvement in controlling movement. Adequate dopamine production is essential for smooth and coordinated movements. Inadequate dopamine levels, as seen in Parkinson’s disease, can lead to tremors, rigidity, and other movement disorders.
Dopamine’s Influence on Pleasure and Reward
Dopamine plays a central role in the brain’s reward system, which reinforces behaviors that lead to positive outcomes. When we engage in activities that bring us pleasure or satisfaction, the brain releases dopamine, reinforcing those behaviors and motivating us to repeat them. This system plays a crucial role in learning, motivation, and addiction.
Dopamine’s Impact on Mental Health
Dopamine abnormalities have been implicated in various mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and depression. In schizophrenia, there is an excess of dopamine activity in certain brain regions, while in ADHD, there may be a deficiency in dopamine signaling. In depression, the balance of dopamine and other neurotransmitters is often disrupted.
Dopamine’s Role in the Body’s Stress Response
In addition to its central role in the brain, dopamine also functions as a hormone in other parts of the body. During stress, dopamine is released from the adrenal glands, contributing to the body’s “fight-or-flight” response. This response helps prepare the body to deal with perceived threats.
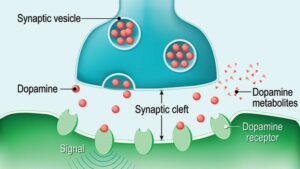
Dopamine Receptors: The Gateways for Dopamine’s Action
Dopamine receptors are specialized proteins found on the surface of nerve cells. When dopamine molecules bind to these receptors, they trigger a cascade of biochemical events that alter the activity of the receiving neuron. Dopamine receptors are crucial for the brain’s ability to process and respond to dopamine signals.
Dopamine Drugs: Targeting the Dopamine System for Therapeutic Effects
Several medications target the dopamine system to treat various conditions. Levodopa, a precursor to dopamine, is used to treat Parkinson’s disease. Dopamine agonists mimic the action of dopamine, while dopamine antagonists block dopamine receptors. These drugs are used to treat conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, restless legs syndrome, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and nausea.
Dopamine Supplements: Investigating their Potential Effects
While dopamine itself cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, its precursor molecule, tyrosine, can. Tyrosine is an amino acid found in protein-rich foods, and tyrosine supplements have been studied for their potential to boost dopamine levels in the brain. However, scientific evidence suggests that tyrosine supplementation may not significantly impact physiology, thought, or behavior.
Conclusion: Dopamine – A Multifaceted Neurotransmitter with Profound Implications
Dopamine is a fascinating and multifaceted neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in various aspects of human functioning. Its involvement in movement, pleasure, reward, mental health, and stress response highlights its profound impact on our lives. Understanding dopamine’s mechanisms and potential imbalances can aid in identifying and addressing underlying health conditions.
 Dopamine: The Neurotransmitter Orchestrating Movement, Pleasure, and Behavior
Dopamine: The Neurotransmitter Orchestrating Movement, Pleasure, and Behavior
Dopamine: The Master Conductor of Our Brain
Dopamine, a small molecule with a big impact, is a neurotransmitter that plays a pivotal role in regulating our emotions, movement, and motivation. It is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because of its role in the brain’s reward system.
Dopamine’s Role in Movement
Dopamine is essential for smooth and coordinated movements. It helps control the timing and force of our muscle contractions, allowing us to perform complex tasks with ease. When dopamine levels are low, we may experience tremors, rigidity, and difficulty with balance. This is why dopamine deficiency is a hallmark symptom of Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement.
Dopamine’s Role in Pleasure and Reward
Dopamine is the key player in the brain’s reward system, which is responsible for reinforcing behaviors that lead to positive outcomes. When we engage in activities that we find pleasurable, such as eating delicious food, listening to music, or spending time with loved ones, dopamine is released in the brain’s reward circuitry. This surge of dopamine reinforces the behavior and motivates us to repeat it.
Dopamine’s Role in Mental Health
Dopamine imbalances are implicated in a range of mental health conditions, including:
-
Schizophrenia: Excessive dopamine activity in certain brain regions is thought to contribute to the hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking that characterize schizophrenia. Nutritional and functional medicine support plays a huge impact in reducing symptoms.
-
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Dopamine deficiency is thought to play a role in the inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are hallmarks of ADHD.
-
Depression: Dopamine levels are often low in people with depression. This may contribute to the feelings of sadness, anhedonia (lack of pleasure), and apathy that are characteristic of the condition.
Dopamine’s Role in the Stress Response
Dopamine also plays a role in the body’s stress response. When we perceive a threat, dopamine is released from the adrenal glands, contributing to the “fight-or-flight” response. This response helps prepare the body to deal with danger by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing.
Dopamine Receptors: The Gateways to Dopamine’s Effects
Dopamine receptors are specialized proteins found on the surface of nerve cells. When dopamine molecules bind to these receptors, they trigger a cascade of biochemical events that alter the activity of the receiving neuron. Different types of dopamine receptors have different effects, contributing to the wide range of functions that dopamine regulates.
Dopamine Drugs: Targeting the Dopamine System for Therapeutics
Several medications target the dopamine system to treat various conditions. Levodopa, a precursor to dopamine, is used to treat Parkinson’s disease. Dopamine agonists mimic the action of dopamine, while dopamine antagonists block dopamine receptors.
Dopamine Supplements: Investigating Their Potential Effects
While dopamine itself cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, its precursor molecule, tyrosine, can. Tyrosine is an amino acid found in protein-rich foods, and tyrosine supplements have been studied for their potential to boost dopamine levels in the brain. However, scientific evidence suggests that tyrosine supplementation may not significantly impact physiology, thought, or behavior.
Dopamine – A Multifaceted Neurotransmitter with Profound Implications
Dopamine is a fascinating and multifaceted neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in various aspects of human functioning. Its involvement in movement, pleasure, reward, mental health, and stress response highlights its profound impact on our lives. Understanding dopamine’s mechanisms and potential imbalances can aid in identifying and addressing underlying health conditions.
References
-
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Dopamine: Your Brain’s Reward System. [Online] Retrieved from: https://nida.nih.gov/publications/drugs-brains-behavior-science-addiction/drugs-brain
-
Oxford Medicine Online (OMO). Dopamine. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.psy.ox.ac.uk/news/oxford-researchers-offer-new-insights-into-the-function-of-neurotransmitter-dopamine
-
Mayo Clinic. Dopamine: How It Works and What It Does. [Online] Retrieved from: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/22581-dopamine
-
- Dopamine: The Neurotransmitter That Drives Our Behavior https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16106242/
- Dopamine: A Key Neurotransmitter in Reward, Addiction, and Parkinson’s Disease https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34389279/
- The Role of Dopamine in Motivation and Reward https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3032992/
- Dopamine and the Brain’s Reward System https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2958859/
- The Neurobiology of Dopamine: Implications for Psychiatric Disorders https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7911410/
Hypnotherapy
- The Effectiveness of Hypnotherapy in the Treatment of Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17558718/
- Hypnotherapy for Smoking Cessation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31198991/
- The Efficacy of Hypnotherapy for Anxiety Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31251710/
- Hypnotherapy for Weight Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35108492/
- Hypnotherapy for Performance Enhancement https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35140655/
Hypnotherapy and Dopamine
- Hypnotherapy Enhances Dopamine Release in the Nucleus Accumbens of Healthy Volunteers https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16165291/
- Hypnotherapy Modulates Dopamine Function in the Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1289956/
- Hypnotherapy Activates Dopamine D2 Receptors in the Brains of Individuals with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15121489/
- Hypnotherapy Increases Dopamine D1 Receptor Binding in the Prefrontal Cortex of Individuals with Generalized Anxiety Disorder https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31251710/
- Hypnotherapy Stimulates the Release of Dopamine in the Hypothalamus, Modulating Hunger and Satiety Signals https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2710609/
-
Kandel, E. R., Schwartz, J. H., & Jessell, T. M. (2000). Principles of neural science (4th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Haber, S. N., & Knutson, B. (2010). The reward circuit: Linking brain stimulation and psychological phenomena. Neuron, 67(5), 815-840.
-
Di Chiara, G., & Bassareo, A. (2000). The dopamine reward system: Anatomical, neurochemical and functional aspects. Progress in Neurobiology, 62(6), 315-350.
-
Schultz, W. (2002). Getting formal with dopamine and reward. Neuron, 36(2), 241-263.
Dopamine: A Neurotransmitter Orchestrating Well-being and Health
Dopamine, a ubiquitous neurotransmitter, plays a pivotal role in shaping our mental and physical health, influencing a wide range of functions from movement control to pleasure and reward. It acts as a chemical messenger, bridging the communication gap between nerve cells throughout the brain and the body.
A Master Conductor of Bodily Functions
Dopamine’s influence extends far beyond its role in movement coordination. It plays a crucial role in the brain’s reward system, a network of neurons that reinforces behaviors that lead to positive outcomes. As we engage in activities that bring us pleasure, satisfaction, or a sense of accomplishment, dopamine surges, reinforcing these behaviors and motivating us to repeat them. This system underlies learning, motivation, and addiction, driving us towards activities that promise to increase dopamine levels.
Dopmaine a Regulator of Emotional Well-being
Imbalances in dopamine signaling have been implicated in various mental health conditions. Schizophrenia, for instance, is characterized by an overactive dopamine system, while ADHD may be linked to underactive dopamine signaling. In depression, dopamine levels are often disrupted, contributing to the associated symptoms of anhedonia (lack of pleasure) and apathy.
Dopamine – A Stress Management Ally
Beyond its central role in the brain, dopamine also functions as a hormone, particularly during stress situations. As we perceive threats or challenges, dopamine is released from the adrenal glands, preparing our bodies for the “fight-or-flight” response. This response involves increased heart rate, breathing, and muscle tension, preparing us to either confront the threat or flee from it.
Unlocking Dopamine’s Benefits Through Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support healthy dopamine production and contribute to overall well-being. Here are some key food groups that are particularly beneficial for dopamine synthesis:
-
Protein-rich foods: Protein provides tyrosine, a crucial amino acid for dopamine production. Sources of protein include meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
-
Fruits and vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants and other nutrients that support brain health and may contribute to healthy dopamine levels. Berries, dark leafy greens, and citrus fruits are particularly beneficial.
-
Whole grains: Whole grains provide fiber, which helps stabilize blood sugar levels and may promote healthy dopamine function. Opt for whole-wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, and oats.
-
Healthy fats: Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, olive oil, and nuts, are essential for brain function and may support dopamine production. Include healthy fats in moderation, such as with salads, avocado toast, or nuts as a snack.
Nurturing Dopamine Well-being Through Holistic Approaches including Hypnotherapy, Counselling, CBT, EFT, RTT, Mind Coaching & Psychotherapy
Claire Russell Nutrition, Hypnotherapy and Therapy offers a comprehensive approach to supporting healthy dopamine levels and overall well-being. As an experienced nutritionist, Claire can help you:
-
Create a Personalised Nutrition Plan: We’ll tailor a nutrition plan that incorporates the beneficial foods mentioned above while considering your individual needs, preferences, and any underlying health conditions.
-
Address Underlying Emotional Factors: We’ll explore the emotional and psychological factors that may contribute to dopamine imbalances, guiding you towards stress management techniques and strategies for emotional well-being.
-
Incorporate Complementary Therapies scientifically proven: We’ll consider using complementary therapies such as counselling, hypnosis and clinical hypnotherapy, which can help address emotional and psychological issues, with subconscious thoughts and belief systems that may affect your dopamine balance.
Claire Russell Therapy ONLINE, Limerick & CORK: Addressing Diverse Health Concerns
Our multi dimensional expertise extends to supporting children, teenagers as well as adults facing a wide range of health concerns, including:
-
Addictions: We’ll help you develop strategies and help you overcome a wide range of addictive behaviours and promote healthier coping mechanisms.
-
Anxiety: We’ll provide support and guidance to manage anxiety symptoms and cultivate a sense of calm and well-being.
-
Autoimmune diseases: We’ll help identify dietary, mental and emotional triggers that may exacerbate autoimmune conditions and support overall immune health.
-
Digestive issues: We’ll tailor a personalised nutrition plan to address digestive complaints and promote gut health, which is crucial for dopamine production.
-
Depression: We’ll work with you to address the various underlying factors contributing to depression and support you in developing healthy coping mechanisms and strategies for emotional well-being, and good mental health.
-
Eating disorders: We’ll provide personalised guidance on nutrition, addressing distorted thoughts, conscious and subconscious beliefs and behaviours related to food and body image, and promoting healthy eating habits that support overall well-being.
By understanding the role of dopamine in our lives and adopting holistic approaches that address both nutrition and emotional well-being, we can empower ourselves to achieve optimal physical and mental health.
Contact Claire Today on: 087 716 8844
Email: clairerusselltherapy@gmail.com

 Dopamine: The Neurotransmitter Orchestrating Movement, Pleasure, and Behavior
Dopamine: The Neurotransmitter Orchestrating Movement, Pleasure, and Behavior